Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is accompanied by severe soreness and other unpleasant symptoms, therefore it gives the patient severe discomfort. In order to cope with the pathological process, it is necessary to establish the causes that led to its occurrence. Let’s see how it manifests itself, how to treat stomatitis in the mouth in an adult or a child, what types it is by etiology, localization, and other criteria, and also consider the main preventive measures to prevent it.

What is a disease
This is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth. Pathology can be localized both in visible areas (lips, cheeks) and in the pharyngeal region, where it is rather difficult to detect sores. A characteristic feature of the disease is that it recurs periodically (every few years or even monthly). The frequency of inflammation depends on the immune defense of a particular person and other features of his body.
Is stomatitis contagious
The infectiousness of the disease is determined depending on the factors that provoked its appearance. For this reason, it is important first of all to consult with a doctor who will definitely conduct the necessary studies using special tools, prescribe tests, and compare the patient’s complaints with external manifestations. Thus, it is possible to find out how contagious the disease is only after undergoing a series of diagnostic procedures.
For example, if stomatitis in the mouth is caused by thermal exposure, an allergic reaction to any food product, the intoxication of the body, and injury, then fears of infecting others are in vain. However, the disease is actively transmitted when it is provoked by infection with pathological agents, which leads to inflammation.
Why does a child often have stomatitis in the mouth, and does it occur in an adult for the same reasons? Small patients are more susceptible to infection through toys and household items. Recently transferred diseases lead to a decrease in immune defense and therefore increase susceptibility to pathogens. The same is true for people who have been taking antibacterial drugs for a long time in the treatment of other pathologies.
How stomatitis manifests itself at the very beginning
In most cases, the disease is easy to self-diagnose with a visual examination. However, this does not mean at all that you should neglect visiting the dental office and diagnose yourself based on the presence of characteristic signs (which causes stomatitis in the mouth of a child and an adult, as well as the required methods of treatment, unfortunately, are not taken into account).

Common external manifestations:
- Slight swelling, accompanied by redness of the soft tissues (at the very initial stages);
- Swelling of the pathological area with a burning sensation (as the inflammation spreads);
- The formation of a whitish spilled spot.
Having discovered the symptoms listed above, many immediately diagnose themselves and run to the pharmacy for well-known ointments and other external agents, pills that are on everyone’s lips. Even the most expensive and effective medicines can not help when they are chosen incorrectly. If the patient does not have a medical education, he will not be able to accurately establish the etiology of the disease, and therefore determine the direction of therapy in a particular case.
Do not be lazy, it is better to immediately make an appointment with the dentist. The sooner measures are taken to eliminate ulcers, the faster they will pass.
Causes
There is a list of the main factors that lead to the development of inflammation of the mucosa. What causes and why stomatitis constantly appears in the mouth in children and adults:
- Damage to soft tissues as a result of mechanical impact. For example, you can cut yourself with fragments of a tooth, solid food, or chicken bone. Usually, wounds heal quickly and without negative consequences. However, if the immune system is weakened, complications can occur.
- Dryness of the mucosa due to the use of rinses and toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Eating foods high in carbohydrates with a deficiency of vitamins and minerals.
- Allergy to certain foods, chemicals, pollen, etc.
- Hormonal imbalance in women is associated with certain phases of the menstrual cycle, puberty, childbearing, and childbirth.
- hereditary predisposition. If parents or other generations of relatives suffered from this disease, the risk of developing the disease increases significantly.
- Bad habits. Under the influence of alcohol and nicotine, the microflora is disturbed, so the body is not able to fully resist pathogens and quickly recover.
- The presence of viruses and other microorganisms in a “sleeping” state after suffering diseases that are activated when immunity is reduced.
- Stressful situations, and depression, from which stomatitis in the mouth can really appear.
Symptoms of stomatitis in the mouth
Pathology is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Soreness;
- Redness of the damaged areas, associated with swelling and burning;
- The appearance of a whitish spot in the form of an oval, covered with a thin film (if stomatitis is caused by bacteria);
- Profuse salivation;
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- Bleeding gums;
- Loss of sensitivity of the tongue and lips (in advanced cases).
As a rule, the symptoms completely disappear after 1-2 weeks. Sometimes the disease can go away in a few days. The duration and severity of the inflammatory process primarily depend on the causes of its occurrence and the patient’s immunity.
How to Use and Brush Your Teeth with an Electric Toothbrush
What can be stomatitis
There are many forms of the disease. The assignment of pathology to one type or another depends on its etiology and associated symptoms.
Aphthous
Aphthae are small ulcers up to 0.5 cm in diameter. At first, unclear blisters are observed on the affected area, which then burst and turns into extensive whole ulcerations. This type of stomatitis is caused by viruses, bacteria, or chronic diseases of the internal organs.
Subspecies:
- Fibrinous (with an insufficient circulation of blood flow);
- Necrotic (tissue death);
- Granular (with damage to the salivary glands);
- Deformation (violation of the integrity of the sky);
- Cicatricial (damage to the connective tissue).
Herpes
The herpes virus type 1 actively spreads in the epithelium and lymph nodes of young children and then affects the skin and mucous membranes. In this case, an increase in body temperature and a sharp decrease in immunity can be observed.
Throat
It is diagnosed in 1/5 of all patients with stomatitis. Yellowish ulcerations can be observed on the root of the tongue, in the throat, and on the palate. In severe cases, difficulty breathing occurs due to swelling of the ligaments. This type is often associated with a runny nose and cough.
Ulcerative
Ulcers are formed in the absence of high-quality and timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, as well as in the case of poisoning. When the patient chews or speaks, there is severe pain and itching.
Spicy
Appears unexpectedly, accompanied by a very high body temperature and swollen lymph nodes. With the recurrence of the pathological process, it flows into a permanent form, and then the body will be able to quickly cope with pathogens.
Chronic
Why does stomatitis in the mouth appear often, even if the treatment is carried out efficiently and in a timely manner? When the immune system is very weak, the disease comes back again. In most cases, this happens in the autumn-winter period and early spring, because there is a deficiency of vitamins in the body. The situation is complicated by the widespread acute respiratory infections.
Catarrhal
Ulcerative formations for this type are not typical. Only slight swelling is visible, there is slight redness. The pain is practically not felt, and the body temperature is kept within the normative values. Small patients may suffer from fever in the first days, but it quickly passes.
Allergic form
In the presence of a predisposition to certain foods, chemicals, pollen, and other external factors, dryness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity appears. Taste buds are not sensitive enough, soft tissues become inflamed.

Stomatitis in a child
The child’s body is unable to fully withstand the effects of external factors. That is why pathology is common mainly among young patients.
Viral type
There are many viruses that can provoke an inflammatory process. Not only the severity of the course of the disease but also the speed of recovery depends on the type of pathogen. There is pain when swallowing and chewing food, and the body temperature rises. Parents can feel for enlarged lymph nodes. A runny nose and cough appear, so the disease can be mistakenly confused with an ordinary seasonal cold.
Candidal type
It develops when pathogenic bacteria enter the oral cavity. Children often put various objects into their mouths and do not practice good hand hygiene. Some parents forget or do not properly wash fresh fruit. All of this provokes inflammatory processes in soft tissues. Ulcers and a whitish coating of a curdled consistency appear. If you try to erase it, the ulcers will begin to bleed.
Where is stomatitis in the mouth: localization of the pathological process
Inflammation can develop in various parts of the mucosa, which greatly complicates self-diagnosis. The primary task of the doctor is to determine exactly where the lesions are located.
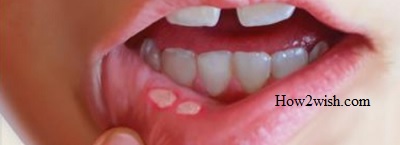
On the lip
Sensitive skin is very susceptible to pathogens. The affected areas at first look like bubbles filled with cloudy contents and then turn into sores. On average, they heal in about 3-4 days. If the patient sees a doctor in a timely manner and undergoes high-quality treatment, the disease will completely disappear in 1-2 weeks. Causes of the first symptoms of stomatitis in the mouth in children and adults, when the disease is localized in this area:
- Weathering in bad weather, dryness during the hot season or during the heating season;
- Thermal burns;
- Activation of the herpes virus;
- Chickenpox or scarlet fever, recently transferred by the patient;
- Pregnancy.
On the gum
This is the most common type of inflammatory process that people of any age can experience: newborn babies, preschoolers, and adults. In schoolchildren, this type of pathology is diagnosed less frequently.
Early diagnosis allows you to accurately determine the localization of the disease. With untimely detection of stomatitis, it passes to the entire surface of the mucous membranes, including the inside of the cheeks, as well as the lips. Small cracks are clearly visible in the corners of the mouth.
In the sky
In most cases, babies are found with this type of pathology. If we deal with the etiology of the disease, the causes of the development of stomatitis in young children are associated with the inability and inability to follow simple hygiene rules. Preschoolers pick up toys and other objects from the floor, and the ground on the street, and taste everything because of their curiosity. Because of this, a certain environment is formed in the oral cavity, favorable for the reproduction and active life of pathogenic microorganisms. The first clear sign of the disease is a visible whitish coating on the palate and surrounding soft tissues.
On the tongue
Along with the most common causes (for example, poor hygiene), this type of pathological process is also caused by sleep disorders. This is most often characteristic of young children who have little rest, do not sleep well, are constantly worried, and therefore experience tremendous stress. As a result, there is a sharp decrease in immunity, so there are health problems, including inflammatory ones.
The first signs of stomatitis in the mouth in adults and children: how to treat it
There are many ways to cope with an unpleasant disease. However, patients should not self-medicate, or purchase medicines on the recommendations of friends or reviews on the Internet. Only a doctor can develop an effective therapeutic regimen. The specialist can determine the exact causes of the disease, determine its type, select the appropriate drugs, and give recommendations for proper care.

Home treatments
Most patients, after experiencing discomfort in the oral cavity, prefer not to visit the dental clinic, but try to cope on their own. Rinses with various compositions, enhanced hygiene, and other methods come to the rescue. Of course, sometimes they really show positive results, and the disease recedes, but it is impossible to give any guarantees of the effectiveness of self-treatment at home. The selection of medicines should be carried out by an experienced physician.
Folk remedies for manifestations of stomatitis in the mouth
It’s no secret that there are natural antiseptics that allow you to fight inflammation of the mucous membranes. These include chamomile flowers, propolis, garlic, chicory, and so on. The use of such funds can really alleviate the symptoms if the disease is caused by a decrease in immunity and a lack of vitamins. When inflammation is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms and other serious pathogens, traditional medicine is unlikely to help. The best option is to use herbs along with medications prescribed by the dentist as part of complex therapy.
Treatment at the doctor
Contacting a specialist is the most correct solution in the case of stomatitis. Only a physician is able to correctly recognize the external manifestations of the pathology, conduct high-quality diagnostics, develop a treatment regimen, and select the appropriate medicines in a particular case. Treatment should be aimed not only at getting rid of the symptoms, but also at eliminating the provoking factors that led to the development of the disease.
Preventive measures
Prevention of the occurrence of stomatitis in the mouth in adults and children, the identification of the causes, symptoms, and effective treatment of which takes time, the professionalism of the doctor, and high-quality comprehensive diagnostics, can prevent the development of pathology, and therefore save the patient from discomfort.
Useful recommendations that will help maintain the health of the oral cavity and prevent the appearance of pathology:
- Visiting the dentist at least once a year for preventive purposes;
- Timely treatment of dental diseases;
- High-quality daily oral hygiene;
- Washing your hands regularly, especially before eating;
- A completely balanced diet, the rejection of foods rich in “fast” carbohydrates;
- The correct selection of products and accessories for hygienic care of the oral cavity.
Thus, the tactics of treating the disease primarily depend on the causes of frequent stomatitis in the mouth in an adult or a child. If you approach your health with all responsibility and follow preventive measures, an unpleasant inflammatory process, accompanied by soreness and other discomforts for the patient, can be avoided.