The predominance of simple carbohydrates in the diet, as well as the abuse of tea and black coffee, is a problem in terms of maintaining oral hygiene. Especially in cases where smokers adhere to such a regimen, the deposition of plaque on the surface of the enamel coating and in periodontal pockets is almost guaranteed. Regular prophylaxis at home is usually limited to brushing your teeth and does not always help to restore the natural state and completely remove pathogenic microelements. What are tartar, where do they come from, how and from what are they formed, and what causes should you pay special attention to?

General view
Microbes that settle on the enamel while eating food find themselves in a warm and humid environment, optimally suited for their further transformation and reproduction. If no removal has been carried out within fifteen hours since the last diet, the mineralization process begins in the structure, characterized by its gradual hardening. After a week, the cycle is already irreversible, and after six months, the dead microorganisms actually become stone, acquiring a hue ranging from yellow to brown-brown.
From a biochemical point of view, tartar is 30% organic compounds, the volume of which is consistently reduced as the content of inorganic components increases. In each individual case, the composition depends on the length of the conversion period. At the same time, it should be borne in mind that ignoring the recommendations for hygienic care, even for several days, leads to the formation of a rough film that contributes to the accumulation of even more plaque. In addition, abnormal formations provoke inflammatory processes in the gum tissues, stimulating the production of fluid saturated with salts and proteins, which increases the population of pathogenic microorganisms.
Types of tartar
In accordance with the classification adopted in dentistry, the main criterion for the difference is the location of the stony structure. Based on this, distinguish:
- Supragingival – localized in the area of the enamel coating, not covered by the gum.
- Subgingival – formed in the inner part, which poses a particular risk in terms of timely diagnosis and treatment.
The pace of development of pathology
The intensity of accumulation is determined by individual factors, including hygiene skills, as well as concomitant circumstances. The catalyst, as a rule, is non-compliance with the basic rules of oral care. The formation of a thickened sticky film stimulates the growth of the number of bacteria that linger in the problem area, which ultimately causes negative changes. The transformation into a dense structure usually takes up to six months, which leads to a recommendation to undergo a preventive examination at the same time.
Symptoms of tartar
Signs that indicate the appearance of plaque on the teeth include the following characteristic symptoms:
- Darkened areas of the gingival contour, more often on the lingual side, remain even after cleaning with an abrasive paste.
- Changing the shade of the enamel coating and the occurrence of persistent bad breath.
- Increased gum bleeding under the influence of mechanical stress, including not only hygiene procedures but also food intake.
- Increased susceptibility to temperature changes, and the use of sour and sweet foods.
- Formation of deep and widened pockets, as well as partial exposure of the root region of individual units.
It should be noted that an independent visual examination allows the establishment of only the presence of external, supragingival tartar, while the subgingival form is diagnosed only during a clinical examination.
Potential Complications
Patients who are faced with the consequences of an abnormal condition are not only concerned about the deterioration in the aesthetics of a smile or the appearance of an unpleasant odor – although these problems often cause a lot of inconveniences. With a long course of pathology, there is a possibility of developing more severe conditions, including diseases such as caries, gingivitis, and periodontitis. Lack of timely medical intervention can eventually lead to tooth loss.
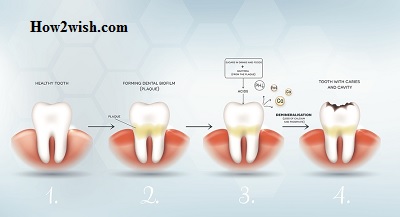
Considering what causes tartar and what it consists of, it is not difficult to determine how harmful and dangerous this condition is. Deposits formed from harmful bacteria reduce local immunity, preventing the body from suppressing pathogenic properties and fully resisting possible infection. The result of the vital activity of cells, oxidized as they transform and acquire a stony structure, is the destruction of the enamel coating that protects the elements of the series from external influences, as well as the occurrence of inflammatory processes in mucous tissues. Stones in the gums, in turn, break the connection between the root part and the periodontium, which leads to a weakening of the fit, loosening, and loss of teeth.
Provoking factors
The reasons for the onset of a pathological condition include:
- Insufficient or improper oral care.
- Metabolic disorders, including those caused by chronic diseases.
- The anomalous position of individual units.
- The presence of rough areas on the surface of the enamel.
- Prolonged wearing of corrective structures, including braces.
- The predominance in the diet of food with a soft texture is saturated with carbohydrates.
- Malocclusion leads to the incorrect distribution of chewing load.
- Abuse of bad habits, including smoking.
- General deterioration of the functions of the immune system.
In dental practice, the causes of plaque formation and the appearance of tartar are most often two factors – neglect of the basic rules of hygienic care, as well as a long history of smoking.
Preventive actions
It is no secret that the prevention of any pathology requires much less cost than its subsequent treatment. This rule is relevant both in terms of financial costs and in terms of the time that you have to spend visiting a dental clinic. Within the framework of the problem under consideration, one of the main preventive means is the usual cleaning of the oral cavity.
How to brush your teeth properly
- The list of medical recommendations on this habitual hygiene procedure is not limited to the advice to use a brush and paste twice a day:
- Movements should be accentuated and directed from the gingival margin to the edge of the crown – a kind of “sweeping” gesture.
- First, the front element of the row is processed, then the inner side, including deeply located areas.
- During the cleansing of chewing units, one should alternate reciprocating and circular passes, including those covering the “eights”.
- The duration of the procedure is at least three minutes, for which you can use an hourglass or a timer on your smartphone, or select a music track with the appropriate timing.
Patients who have been diagnosed with a chronic predisposition that explains what causes plaque and why stones appear on the teeth are recommended to brush after each diet.
Choosing a toothbrush
Another important factor that requires the advice of a qualified specialist. When choosing personal accessories for care, you should pay attention to the stiffness of the pile and the presence of rubber plates that help remove deposits and polish the surface of the enamel.
In childhood, as well as during periods of development of inflammatory processes, accompanied by bleeding and soreness of the gums, soft samples should be used. The hard version is suitable for use no more than once or twice a week, however, it is excluded if there are areas of bare root neck, since an incorrectly set movement technique can provoke a wedge-shaped defect. It is also worth noting that the predisposition to pathology provides for regular replacement of the brush, in some cases every month.
Irrigator
Another option contributes to the prevention of the causes of the formation of stones in the teeth. The use of a device for supplying water or a saturated solution under pressure helps to eliminate deposits at the initial stage of formation, that is until they are mineralized. This treatment, combined with regular cleaning and flossing, reduces the likelihood of developing a pathological condition.
Dental floss
A convenient tool for cleaning interdental areas, which often accumulate the remnants of food consumed. In the process of application, it is important to be careful and careful, since excessively intense efforts can lead to damage to the gum tissue, bleeding, and the formation of small wounds open to infection.
Use of rinse aid
Special formulations with an antibacterial effect also help maintain oral hygiene. When choosing the right option, you should focus not only on the smell of the liquid but also on the list of components contained in its structure. It is also important to remember that mouth rinses are not a substitute for all other procedures and should be considered as an adjunct to regular brushing.
What Is Fluoride? Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, and Safety
Tartar removal methods
In the Dentika dental centers, various methods and technologies are used to quickly and painlessly get rid of the petrified plaque on the enamel. Consider the current solutions recommended by experts.

Hardware ultrasonic processing
A popular method based on the use of a device that generates directed ultrasound waves with a frequency of 16 to 45 thousand hertz. The wave effect contributes to the crushing of stony deposits, has an antiseptic effect on adjacent tissues, and helps to eliminate formations that violate the visual aesthetics of a smile. With the increased sensitivity of the teeth, local anesthesia is used, which excludes discomfort for the patient.
Laser removal
An innovative technique that allows non-contact exposure to remove tartar, which means not only efficiency and painlessness but also absolute safety. In terms of the result achieved, it is comparable to an ultrasound procedure. The only drawback is the higher cost associated with the cost of purchasing the device.
Airflow
A mechanical cleaning method that involves supplying an air jet saturated with an abrasive mixture to the problem area under pressure. It is equally effective both in terms of removing soft plaque and, if necessary, removing large stony deposits, however, it is inferior in thoroughness to the two previous options.
Manual technique
The instrumental method implemented “the old-fashioned way”, today is no longer included in the standard list of proposed procedures. The reason is the negative consequences, the onset of which can provoke the repulsion of stones, as well as the soreness of the physical impact, requiring the use of local anesthesia. The high probability of injury precludes cleaning with periodontitis.
Which option to choose
The decision is made jointly with the attending physician based on the indications of the clinical picture obtained as a result of preliminary diagnostics. Techniques that exclude side effects and help to remove abnormal formations in full are considered the best choice.
What to do after the procedure
Regardless of the method chosen, the final stage of processing involves grinding and polishing the enamel. If necessary, fluoridation is allowed, as well as the application of an additional protective composition to the teeth, which excludes infection or plaque accumulation. For two weeks after visiting the dentist, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Abandon abrasive pastes with a whitening effect in favor of formulations designed for sensitive tissues and with an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Use rinses with soothing and astringent properties.
- Exclude from the diet spicy foods, as well as foods and drinks containing aggressive pigmenting components.
- Refrain from smoking.
Are there traditional ways to remove tartar?
If we talk about the effectiveness, similar to clinical treatment – no. Traditional recipes are relevant only in cases where the plaque structure has not yet entered the mineralization phase and is characterized by friability and a light shade. In such situations, it is recommended:
- Including grated radish with lemon in the diet, as well as using its pieces as a cleaning agent.
- Mitigation of abnormal build-up with hydrogen peroxide, followed by cleaning and rinsing with soda solution.
- Using fresh, but already cooled coal ash as a tooth powder.
With regard to safety and productivity, it is objectively difficult to guarantee the achievement of the desired result in each individual case. In general, doctors tend to recommend not to self-medicate, but undergoing complex diagnostics and therapy, excluding more serious consequences.
Contraindications for stone removal
Hardware disposal of stony deposits may be limited for medical reasons:
- The presence of installed prostheses and braces.
- Previous implantation, including the use of pacemakers.
- Diagnosis of dangerous infections, including tuberculosis and HIV.
- Oncology at different stages of development.
- Pregnancy in the first and third trimesters.
- Interchangeable bite period.
The final decision on the choice of technique, including taking into account both existing and possible clinical contraindications, is made after consultation with a qualified dentist.
Summarize
A well-structured diet, regular exercise, the absence of bad habits, and the implementation of recommendations for hygienic oral care are key factors in avoiding most pathologies. Knowing what tartar leads to and what needs to be done to avoid its appearance, you can minimize the risk of plaque formation and a mineralized structure that affects not only enamel but also adjacent tissues.