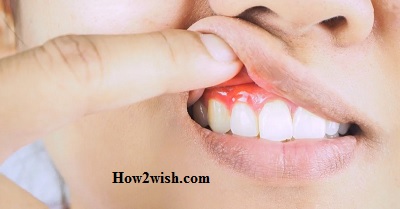
What to do when Gums Have Fallen Away from the Tooth? Recession is a reasonably common problem in patients. They ask doctors why the gum on the tooth has sunk (it is exposed), what to do, and how to raise it and stop the pathological process. There can be several reasons for the phenomenon, as well as methods of treatment – each situation is considered by a dentist-therapist individually so that the diagnosis is accurate and the therapy is as effective as possible.
Why is this happening
The etiology differs from case to case. Infrequent, but one of the most unpleasant options is a genetic predisposition to the disorder. If it is identified, a person will almost inevitably encounter painful dental symptoms, even if he takes meticulous care of his oral health. Other possible reasons why the gums descend, move away from the front, molars, wisdom teeth, and are exposed:
- Poor hygiene (neglect of brushing, flossing, annual professional maintenance, regular visits to the dentist), as a result of which plaque forms on the neck, and later tartar;
- Malocclusion;
- Inflammation of the periodontium (tissues that seal the alveoli), provoking the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria, and subsequently purulent contents in the periodontal pocket;
- Errors in previous orthodontic or orthopedic treatment that can lead to injury;
- Mechanical, thermal, and chemical damage – often pathology is provoked by irritation from the habit of chewing on foreign solid objects, drinking too hot or sour drinks;
- Poor-quality prosthetics, in which the prostheses do not fit snugly enough to the bases or put excessive pressure on soft tissues;
- Hormonal disorders – most often in women aged, experiencing menopause, carrying a child, breastfeeding, or hormonal surges of another etiology;
- Poorly balanced diet – lack of solid foods, vegetables, and fruits, excess of foods rich in fast carbohydrates (white bread, muffins, sweets, some cereals – for example, semolina);
- The age of the patient, which provokes atrophy, is one of the reasons why the gum near the tooth may begin to sink and recede strongly, hurt, and require treatment.
Smokers are also at risk, especially heavy smokers who smoke a pack or more per day. Exposing the necks of their teeth is primarily caused by a large amount of plaque formed as a result of the abuse of nicotine. Often, such patients neglect regular professional (mainly ultrasonic or sandblasting) cleaning, which aggravates the situation and provokes the rapid development of dental pathologies. If a person cannot give up a bad habit, doctors recommend that he be as scrupulous as possible in the issue of hygiene, attend annual preventive examinations, and regularly remove harmful deposits.
Diseases in which the gums move away from the teeth
There are a number of somatic disorders that are risk factors – in their presence, soft tissue loss occurs more often and progresses faster than in healthy people. Recession is not uncommon in patients suffering from:
- Diabetes mellitus of any type;
- Problems with the kidneys, liver, and spinal cord (they can cause circulatory dysfunction in the soft tissues of the oral cavity, as a result of which they do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients);
- Diseases that are accompanied by immunodeficiency states;
- Endocrinological pathologies (disruption of the endocrine glands).
Too frequent and prolonged use of diuretic drugs, prescribed for certain diseases, also contributes to the manifestation of the anomaly, since the necessary nutrients are removed from the body along with the fluid.
Below is a list of dental disorders in which the development of a recession, when a piece of gum leaves near the tooth, can be most likely predicted:
- Periodontitis – inflammation of the periodontium, which is characterized by the destruction of the normal structure of the alveolar process;
- Gingivitis – irritation of soft tissues without violating the integrity of the dental gingival junction;
neoplasms of various etiologies.
How pathology manifests itself: Symptoms
In the later stages of the disease, the patient can observe its consequences with the naked eye:
- Bleeding of the areas surrounding the roots (at first only when eating and cleaning, later – constantly);
- The formation of noticeable cracks;
- Exposure of the tooth necks;
- Swelling and redness of the mucous membranes;
- Loosening, suppuration of periodontal pockets (in advanced cases).
Also, the process is often accompanied by a bitter taste of pus and an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity, which is difficult to disguise and does not go away even from the use of paste, chewing gum, and rinses.
The primary stages of the disease are sometimes asymptomatic, but even in the first days, the patient may feel discomfort. Dentists at the Dentika clinic warn that if you have the slightest discomfort in your mouth, you should make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible since in the early stages of the development of the pathology, its treatment and elimination of the consequences are much easier than when it has already developed sufficiently and brings pain.
How to understand that the gum that has moved away from the tooth has fallen, and how do treat it? You can gently pull the edge of the soft tissue with your finger: even at the beginning of the disease, a slight omission under mechanical action will be noticeable. Therapy in this case can only be prescribed by a professional after a personal examination (there are several options for interventions) – self-treatment is unacceptable here.
Diagnosis of the disease
Despite the fact that the symptoms are most often noticeable even to the person himself, the dentist, when visiting the clinic, is likely to prescribe additional examinations to clarify the diagnosis and prerequisites. It can be:
- Orthopantomogram;
- Radiographic study.
In addition, before choosing a treatment method, it is mandatory to check the depth and condition (for the presence of severe inflammation, and suppuration) of the periodontal pocket. It depends on its results whether conservative therapy can be dispensed with or surgical intervention is required.
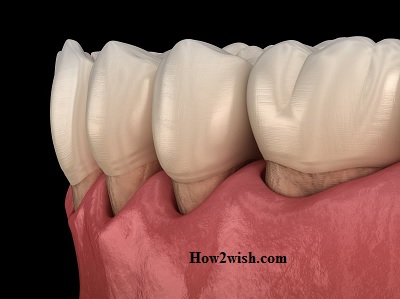
Since often the real cause of tissue atrophy is a somatic disease (hidden or diagnosed), it is highly likely that a deeper examination will be prescribed (the dentist can refer you to a therapist who will prescribe the necessary tests and issue a conclusion). If you do not start timely treatment and do not achieve remission, the recession will most likely return and you will have to get rid of it again.
First aid at home – what to do if the gums sink and teeth are exposed
It is unacceptable to refuse to visit the clinic because in this case, the pathological process will continue – it will not be possible to recover without a doctor completely. However, if it is not possible to make an appointment with a doctor immediately at the time an anomaly is detected, you can slightly delay its progression:
- Use only soft toothbrushes and floss;
- Rinse the oral cavity several times a day with dental (local) antiseptic solutions to prevent the development of severe inflammation;
- Use antibacterial gels;
- Rinse your mouth with anti-inflammatory herbal teas (chamomile, sage, propolis, etc.) or use them as short-term compresses.
It is better not to disturb the painful area, clean it very carefully and not injure the tissues with hard objects (in particular, refuse hard snacks like seeds, chips, or crackers).
How is the treatment carried out if the gum has moved away from the tooth and dropped: what to do and why does it help
Therapy in dentistry consists of two stages. The first is the cleansing of the dentition and getting rid of plaque, which is the root cause of the disease. The second is healing.
Hygienic cleaning can be carried out according to one of three methods:
- Instrumental – now it is rarely used. This method removes stone under the tissues with a special metal scraper. It is considered quite traumatic and in most clinics doctors no longer take it up, offering more modern options as an alternative.
- Ultrasonic – using a scaler (aka scaler) – an instrument that operates with ultrasound. It is often used, and it is able to completely remove solid pathogenic deposits.
- Sandblasting. In this case, under high pressure, the hygienist delivers a solution containing abrasive elements to the treated surface area, which “knocks” the stone off the crowns and allows the cleaning of periodontal pockets. As a result (as a “bonus”), you can even get a slight whitening, by 1-2 tones.
If the situation is not critical, and the disease has not developed to a serious stage, then within a few months after hygienic treatment, the soft tissues completely heal and return to their normal state. Pathogenic bacteria are removed at the same time, and the oral cavity becomes healthy.
Surgical techniques – how to cure a receding gum
If it is strongly separated from the neck during the pathological process, and the periodontal pocket is clearly visible, most likely, the structure of the bone has already changed. In this case, you can not do without surgery – it is performed under local anesthesia. An open or closed curettage is performed (the so-called “curettage”) – a manipulation in which inflamed or necrotic material is removed using a unique tool – a curette. The opened cavity is cleared of purulent exudate, after which it is sutured or restored in one of the following ways:
- Patchwork restoration – plastic surgery using a donor flap from a neighboring site;
- Membrane plasma lifting is a more modern and less traumatic operation that takes more time;
- Installation of a collagen implant that promotes regeneration.
In the most difficult situations, it is impossible to do without the removal of the affected teeth and subsequent implantation or prosthetics.
Related post A Guide to the Best Practices of Cleaning and Care for Your Dentures

The method of treatment is chosen by the attending physician-therapist together with the patient, depending on the indications and severity of the pathology. The specialists of the Dentika clinic always use the best method for a person, the recovery after which will be as short as possible, and the result will be the most satisfying to the request.
Medicines
It is possible to prescribe various drugs:
- Antiseptic;
- Antibacterial;
- Immunostimulating;
- Hormonal.
It depends on the causes of the disease. In some cases, the doctor does not make a final decision but directs the patient for additional examinations. It must be remembered that self-medication is unacceptable here and it is imperative to consult a doctor before taking medications inside.
Complementary Therapies
Usually Gums, consultations are shown. Suppose the pathology has developed due to problems with the bite or position of adjacent teeth. In that case, the attending dentist will refer you to the orthodontist for further therapy (for example, installing braces or aligners). When the cause of the trouble lies in an unbalanced diet, a therapeutic diet is prescribed in addition to the usual manipulations, possibly using dietary supplements (but only a doctor can prescribe them). Some patients are given a prescription for hormonal drugs to eliminate the imbalance, and physiotherapeutic methods of influencing the painful area are also advised.
Recovery forecasts
With timely treatment and adherence to proper nutrition, in most cases, everything gets better over time. Within a few months, the wound heals completely, the periodontal pocket disappears, and the recession ceases to bother. After that, it is advisable to take preventive measures so that it does not return.
Possible Complications
Most often, the situation makes patients worry, and they ask what to do if the gum between the teeth goes down, how to restore it? These are the right questions, to which the doctors of the Dentika clinic are always ready to give a competent answer. However, it happens that people do not go to the dentist, preferring to think that the omission of soft tissue is just a minor cosmetic defect. This is not true: if you start the disease, it, together with the causes of the pathology, can lead to serious consequences:
- Lymphadenitis is a condition in which the lymph nodes (usually in the neck) become inflamed
- Periostitis – inflammation of the periosteum;
- Periodontitis;
- Infectious lesions of the jaw bone.
Preventive measures
It is always easier to prevent a disorder than to cure it, especially when it has already acquired an advanced form. To minimize the risk of recession, when the tooth seems to move away from the gum a little, and then not treat it, not so much is required from the patient:
- Eat right, do not abuse foods high in fast carbohydrates, and eat enough fruits and hard vegetables, as well as foods rich in calcium;
- Maintain the normal state of your immune system;
- Carefully monitor compliance with the rules of daily hygiene (use a brush, and floss);
- Give up bad habits (smoking, frequent consumption of seeds, etc.);
- Systematically undergo professional examinations at dentists and annually perform hygienic cleaning;
- Avoid injuries to the oral cavity and dentition (this is especially true for people involved in contact sports disciplines).
An important recommendation of specialists is to consult a doctor at the first signs of discomfort, without ignoring it: this will help to detect pathology at an early stage of development.
Final Remarks on Gums
There are several answers to the question of why the gum sank and moved away from the tooth, but to answer what to do if it hurts and is uncomfortable, you can succinctly – immediately contact the clinic. Dentika deals with such cases, and our dentists are doing everything possible to eliminate the recession as quickly as possible and minimize the chance of recurrence. Our team consists of experienced doctors, and professionals in their field who help patients significantly improve their quality of life.