Increased (pathological) abrasion of teeth is considered a serious problem, which, in the absence of timely diagnosis and medical intervention, leads to impaired functioning of internal organs and systems. This phenomenon is accompanied by certain symptoms, it depends on the stage of the disease and the condition of the dentition.
Experts identify many reasons leading to erasure. Identification of provoking factors is considered the primary task of the dentist, which determines the direction of therapy. Problems can be avoided by following simple preventive rules.

What is tooth wear
This is a rapid reduction in the volume of hard tissues, which can lead to almost complete wear of the crown parts of the dental units. Pathology can be caused by hereditary predisposition, congenital anomalies, systemic diseases, improperly performed dental treatment, bad habits of the patient, and other possible factors. The problem is observed not only with permanent occlusion but also with milk in children.
In the very early stages, erasure goes unnoticed. Only as the pathological process progresses, the patient once notices that the crowns become smaller or their shape changes. This phenomenon is faced mainly by people aged 30-60 years, their share ranges from 23 to 35%.
Physiological wear abrasion of teeth
This is a natural process that occurs in all people. With age, the grinding of incisors, canines, and molars while chewing food is associated with a more rapid thinning of the enamel. Dental units are constantly exposed to mechanical stress during movement, so-called facets are formed on the surfaces, which are manifested by a reduction in the volume of hard tissues. How quickly this will happen depends on the natural strength of the outer layer, bite characteristics, and taste preferences.
One of the common factors is the transformation of the temporomandibular joint and periodontal fibers associated with adulthood. The grinding of crowns is aimed at replenishing lost functions, that is, it is a compensatory reaction.
Pathological tooth wear
It is also called elevated. We can speak of such a type of erasure in the case when, according to all signs, it differs significantly from the physiological one. The process no longer flows as slowly as with the natural type. In addition to enamel, dentin is affected, and then the pulp layer. In the presence of pathology, the patient has pronounced symptoms.
At the stage of decompensation, the height of the upper third of the face decreases. The functioning of the temporomandibular joint is disrupted, soreness of the masticatory muscles occurs, and the process of chewing food worsens. From the side, an increase in the number of nasolabial, chin folds, and the pushing of the chin forward is especially noticeable. Through facial expressions, a person becomes like an old man.
Due to physical changes, breathing problems appear over time, as the volume of air supplied to the oropharyngeal part gradually decreases. The patient unconsciously begins to stoop, causing the spinal column to suffer. As a result, this negatively affects the condition of all internal organs.
Scientists have found that the transformations occurring above significantly worsen the quality of life, which can be reduced to 10-15 years or even more. That is why the problem requires an immediate response at the earliest stages.
Causes of pathological abrasion of teeth
All factors can be divided into general (for example, hereditary) and local (occlusion anomalies, etc.). Very often, erasure is observed in people with bad habits, especially those associated with professional activities (holding tools in their mouths, biting off threads). The enamel is still strong, but the crowns suffer from systematic external influences.
Why are dental units erased most often:
- Malocclusion;
- Bruxism (gnashing of the jaws, mainly during a night’s sleep);
- Loss of one or more teeth (the load when chewing products is uneven, and entire rows take it upon themselves);
- Wearing poorly installed orthodontic or orthopedic structures;
- The presence on the surfaces of small solid particles (grains of sand, soot);
- Increased fluoride content in tissues;
- Congenital disorders of enamel formation inherited
- Necrosis from excessive consumption of acidic products or interaction with acids at the place of work;
- Endocrinological diseases in history;
- Pathology of the pituitary gland;
- Poor quality regular cleaning.
In addition, diseases such as chronic cholecystitis, fluorosis, thyrotoxicosis, etc. can be attributed to the reasons why teeth are worn down (erased). Enamel becomes less durable, so even a slight physical impact can lead to destruction.
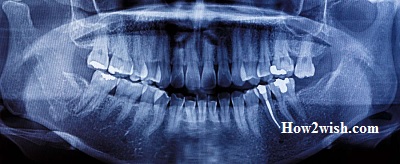
If pathology is detected, the doctor will, first of all, look for provoking factors. The patient will not only have to undergo a course of therapy but also reconsider his lifestyle.
Symptoms of abrasion of teeth
If the erasure is physiological, as a rule, it is not accompanied by discomfort. Yes, and from the outside, it is almost impossible to determine external transformations since dental units are modified very slowly. If there is a pathological process, the anomaly progresses rapidly, the dentin layer is exposed, and hypersensitivity is noted. If you do not contact the dentist promptly-ner, the pulp will be affected.
First of all, there are unpleasant sensations when eating hot and cold food, sour, and sweets. When the enamel is completely worn away, the progression of the disease is even faster, because the dentin is softer than the outer shell, which means it is easier to abrade. The edges of the crowns become sharp and can injure the mucous membranes.
visite: A Comprehensive Guide to the Classification of Diseases of the Oral Mucosa
Increased (pathological) abrasion, and grinding of teeth in the later stages lead to malocclusion, impaired chewing function, changes in the oval of the face, and pain syndrome. If the units are erased, they are smooth, without fissures.
Pathogenesis
The thickness of the enamel in a healthy person is up to 1.7 mm. It is resistant to external influences since the load is evenly distributed over the surfaces. If the thickness of the layer changes, there are no individual incisors, canines, or molars, and there are malocclusion or other violations, in this case, some surfaces are loaded more than others, and the weakened enamel tissue is destroyed.
First, the zones of masticatory tubercles and cutting surfaces become thinner. As the disease progresses, the dentinal canals expand, and the cement and bone fibers of the alveoli hypertrophy. The process of chewing food is disturbed.
Cracks form due to excess load. In severe cases, abrasion leads to pronounced cosmetic defects. Before starting therapy, it is important to accurately establish the causes of this unpleasant phenomenon.
Abrasion of teeth Classification
Each dentist to accurately determine whether the problem natural cure or is a real pathology that requires urgent intervention. What to do if the front teeth are worn down, or erased, depends on what type the phenomenon belongs to. To accurately determine the stage, degree, form, compensatory possibilities, and extent, high-quality diagnostics are necessary for a clinic, but a visual examination by a doctor is not enough. Consider the main erasure groups according to various criteria.
Kinds:
- Physiological. Only enamel is affected.
- Transition. An intermediate stage in which both the outer layer and certain areas of the dentin suffer. It is slightly involved, but this is enough to cause hypersensitivity when eating hot, cold, sour, and sweet, as well as to provoke a narrowing of the lumen of the roots up to their complete obstruction.
- Pathological. Erased not only the enamel layer but also dentinal tissue. In the absence of timely therapy, the process can reach a pulp and provoke irreversible consequences.
By degree
Bushan classification implies the division of pathology into the following types:
- Erasure of the coronal part by a third;
- Decrease by ?;
- Wear more than 66%.
By shape
Varieties:
- Horizontal. Hard tissues decrease in this plane, and the corresponding abrasion of teeth facets is formed. Both jaws may be affected.
- Vertical. Frontal dental units suffer more often, which is associated with the occlusion of antagonists.
- Mixed. There are indications of both options.
By degree of compensation
When dividing according to Gavrilov, the following types are distinguished:
- Compensated. The height of a third of the face from below does not decrease.
- Decompensated. A decline is triggered.
The dental system has high compensatory capabilities. When hard dental tissues contract, the alveolar process is transformed, and the rows are shifted to the pathological zone or areas without occlusion. Depending on the degree of observed changes, classification into the types under consideration follows. In the second case, compensatory transformations are not able to completely correct the anomaly or they do not exist at all.
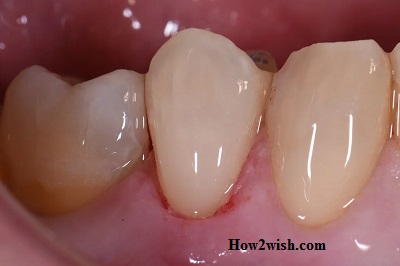
By length
This is the Courland classification. According to this criterion, pathology is divided into the following varieties:
- Localized. Individual units or their groups are erased. It is diagnosed mainly from the frontal side, for example, with a deep bite. There is a local compensation due to the appearance of a hypertrophied alveolar process.
- Generalized. All rows participate, and the bite height changes significantly. Whether the erasure will be compensated by the body is determined by its characteristics.
Abrasion of Teeth Complications
What to do if the teeth are worn out depends on the provoking factors. As discussed above, the lack of timely therapy leads to cosmetic defects and disruption of the chewing process. In addition, other consequences violate the quality of life of patients:
- Inflammation of the gums in the interdental spaces;
- Gingivitis;
- Diseases of the temporomandibular joint;
- Loss of rental units;
- Damage to nerve fibers and muscle tissue;
- Uneven distribution of the load, leading to traumatic articulation;
- Bite anomalies.
Diagnostics
The physiological type of erasure is experienced by most people aged 50 and over. The doctor needs to determine in time when the natural process turns into a pathological one. One of the main methods is the measurement of the actual parameters of the crowns. In addition, it is important to carefully study the shape of the dental units, to determine the areas of contact with antagonists. The height of the crown part is compared with scientifically established age norms.
Diagnostic measures include the assessment of fissures and the state of the enamel. The doctor pays attention to the facial expressions and the appearance of the patient. It is important to talk in detail about the complaints and describe your feelings.
To assess how well the temporomandibular joint functions, electromyography is shown. X-ray examination, electroodontodiagnostics, and other procedures are carried out.
Treatment in dentistry
To eliminate the pathological abrasion of hard tissues of the teeth, you need to establish its cause, and then get rid of it. Next, it is worth restoring the configuration of the dentition. In the early stages, drug treatment may suffice. If the symptoms are pronounced, only an orthopedist will help.
Medicines
The methods used are based on the process of remineralization of the enamel layer. Thus, compensatory reactions are activated, and mineral metabolism in hard tissues is normalized. Specialists prescribe vitamin and mineral products with a high content of calcium and phosphorus. Additionally, pastes are used to reduce sensitivity. If the decay has just begun, and the dentin is not affected, this option for treating tooth abrasion can be very effective.
Orthopedic methods
If the defect is serious, medication alone is not enough, a more radical correction is required. Most often, doctors use tabs and artificial crowns. If any units have fallen out, a bridge structure, clasp prosthesis, or other types are installed. Such therapy allows you to fully restore the functioning of the rows and evenly distribute the chewing load.
Prevention
To prevent pathology, it is necessary to regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations at least once every six months. It is also important to replace defects in dentition promptly. In addition, all experts advise timely correction of bite pathologies already in childhood or adolescence. Orthodontic therapy will help to cope with the abnormal position of the dental units and prevent grinding of the crown part.
It is not necessary to decide what to do when erasing (erasing) hard tissues of the teeth if all the diseases that lead to this are treated. For example, this includes bruxism, mineral metabolism disorders, thyroid pathologies, and problems with the digestive organs.
If the patient is at risk due to professional activities, it is necessary:
- Use personal protective equipment;
- Take a responsible approach to regular hygienic care of the oral cavity;
- Drink courses of vitamins and minerals prescribed by a doctor.
The most important point remains the qualitative diagnosis of the transitional stage between physiological and pathological erasure. For this, regular examinations and timely therapy of identified disorders are shown.
Summing up
What to do if the front lower teeth or upper units are worn out, pain and other unpleasant symptoms appear? First of all, you need to go to the dentist to conduct a thorough diagnosis and identify the exact causes of the pathology. The longer the patient ignores the present signs, the more difficult the consequences for him. In order not to face this phenomenon, it is necessary to observe preventive measures, especially for persons at risk.
Sometimes the enamel wears off due to age-related changes. In this case, we are talking about a natural process. Which group to attribute the problem to, and whether it is necessary to prescribe treatment, should be decided solely by the doctor.