Do you know about Oral Mucosa? As a rule, the development of dental pathologies is a consequence of the progression of abnormal processes occurring inside the human body. Against weakened immunity, the influence of external negative factors increases, leading to the formation of problem areas. The causes of diseases can be different – the symptoms that appear on the tongue, lips, and gums and the results of clinical diagnostics, including those carried out using professional equipment, allow you to determine the source of anxiety. The classification of oral mucosa diseases helps to make a correct diagnosis and timely start therapy that prevents more serious negative consequences.
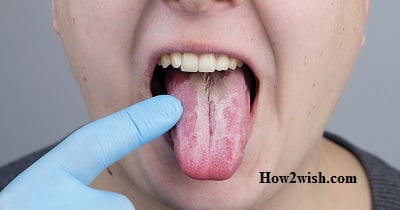
General view
The category of pathological manifestations under consideration is quite extensive. Characteristic signs in this case are inflammatory processes that affect the structure of tissues surrounding the dentoalveolar apparatus. Depending on the type, symptoms may include flushing, swelling, excessive mucus secretion, and the formation of ulcerative and necrotic foci in more complex situations. Prolonged ignoring of the symptoms leads to a deterioration in the general condition of the body, expressed in an increase in body temperature, the onset of pain, a feeling of weakness and anxiety, and an unwillingness to eat.
Factors provoking diseases of the oral mucosa
The patient’s lifestyle and habits, as well as systemic changes that occur in a latent or pronounced form, can increase the likelihood of developing pathologies such as stomatitis, gingivitis, glossitis, etc. Potential sources of risk include:
- Excessive consumption of alcohol and tobacco products.
- Hormonal and immune failure, including those caused by HIV.
- Mechanical tissue damage leads to inflammation.
- Dehydration, or general dehydration of the body.
- congenital predisposition.
- Excessive intake of vitamins of a certain group.
- The influence of the external environment – sharp temperature changes.
- Infection against the background of dental diseases.
- Incorrectly selected diet.
- Self-administration of antibiotics and drugs of strong action.
- Violation of the functional state of internal organs.
Inflammation of the oral mucosa, as a rule, is the result of the impact of negative factors on opportunistic microorganisms that form the natural microflora. Such an influence leads to the development of viral and infectious pathologies, and can also provoke dysbacteriosis, and fungal and inflammatory processes.
Symptoms and their manifestation
The symptomatology characteristic of the diseases of this category, in most cases, allows you to independently diagnose the fact of the presence of deviations from the norm. Notable changes include:
- The occurrence of itching and burning.
- The appearance of pain syndrome.
- The formation of tissue edema.
- Formation of ulcers and abscesses.
- Bleeding gums.
- Violation of the enamel structure.
- Persistent bad smell.
- Feeling weak and tired.
At the first signs of a pathological condition, it is recommended to seek help from specialists. So, in the dental clinic “Dentika” you can undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, which guarantees the accuracy of the diagnosis and the timely start of therapeutic measures.
Types of pathologies
In accordance with the ICD-10 classification for dentistry, treating diseases of the oral mucosa is carried out in four categories. Allocate inflammatory, infectious, viral, and fungal diseases. The treatment plan depends both on the severity of negative symptoms and on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, which are manifested, among other things, in response to certain groups of medications.
Infectious-viral processes
The form of development is directly related to the source of occurrence – for example, the pathological cycles provoked by the introduction of a viral infection are characterized by the following varieties:
- Catarrhal is characterized by pronounced edema and rashes, on the surface of which a gray coating is formed.
- Aphthous – damage to the oral mucosa, associated with the formation of painful blisters, leaving behind areas of erosion.
- Ulcerative – similar in symptoms to the first option, but differs in a more pronounced pain syndrome.
Consider the primary diseases belonging to the category of infectious.
Pharyngitis
An inflammatory process that affects the pharyngeal area, caused both by the introduction of the pneumococcus virus, and by the systematic inhalation of smoke, polluted or cold air. It is accompanied by discomfort when swallowing, exacerbation of susceptibility, and an enduring feeling of perspiration, general malaise, and fever. It is diagnosed by visual examination and by examining a smear sample. In difficult cases, it is treated with antibiotics, but in most situations, a therapeutic course is sufficient, including regular inhalations, rinses, and compresses.

Glossitis
A disease of the mucous surface of the tongue leads to a change in its structure and shade. The likelihood of infection increases with the systematic use of hot or alcoholic drinks and spicy foods, non-compliance with hygiene standards, as well as burn and mechanical damage to tissues. Primary symptoms are characterized by discomfort and a burning sensation. As the pathology develops, areas of redness are formed, the intensity of saliva secretion increases, and taste perception worsens.
The prolonged absence of medical intervention leads to extensive edema, which makes it difficult to perform the usual functions, as well as the formation of growths. The drug treatment of glossitis provides a special dietary regimen that excludes solid foods from the diet.
Gingivitis
Inflammatory disease of the gum mucosa is most often diagnosed in adolescence, as well as in pregnant patients. Various forms of manifestation determine the presence of an additional classification:
- Ulcerative-necrotic – affects the tissues of the oral cavity, provokes an increase in lymph nodes, and is characterized by a pronounced pain syndrome.
- Catarrhal and atrophic – cause swelling, itching, bleeding, an acute reaction to temperature changes, as well as a weakening of the structure.
- Hypertrophic – manifested by a noticeable increase in the size of the gingival papillae, accompanied by bleeding and pain.
The timing of the treatment of gingivitis depends on the stage at which the pathology is detected. The priority task of the dentist is the removal of plaque and the relief of inflammatory processes.
Stomatitis
Infection is carried out in different ways, most often it is the result of mechanical tissue damage. As it develops, characteristic rounded ulcers are formed, localized on the inside of the lips and cheeks, as well as in the region of the root of the tongue.
When diagnosing, it is recommended to treat the oral mucosa, having previously excluded products containing sodium lauryl sulfate from everyday use, since the active ingredient provokes additional irritation. Anesthetics contribute to the removal of pain, and antiseptic and anti-inflammatory compounds are used to remove the film.
Viral pathologies
This category includes abnormal processes triggered by papilloma or herpes viruses, which are also characterized by unpleasant symptoms and require medical intervention. The choice of therapeutic technique depends on the indications of the clinical picture and takes into account individual recommendations based on the results of studying the patient’s history.
Herpes
According to statistical studies, the diagnosis of diseases of the oral mucosa reveals this pathology in 90% of cases. Usually, the pathogen is present in the body in a latent state, manifesting itself only when it is exposed to external triggers, such as impaired immunity, stress, a cold, or surgery.
With a sufficient level of resistance, the appearance of small pimples is observed, localized in the lip area, and persisting for 10-14 days. The anomaly is accompanied by itching and tingling, redness of the tissues, and the formation of small edema. In difficult situations, a characteristic feature is a pronounced pain syndrome associated with the formation of blisters and ulcers. In the early stages, it is recommended to cool the problem area with ice, as well as treat the problem surface with penciclovir or tetracycline ointment.
How Does a Deep Bite Affect Your Oral Health?
HPV (in human papillomavirus )
The disease can manifest itself in various parts of the body, including in the oral cavity. In this case, formations and plaques of a light shade are observed, visually resembling cauliflower. With prolonged development, negative consequences are possible, such as a change in the voice timbre and a violation of the respiratory function associated with a spread in the throat region.
Modern techniques do not completely cure papilloma, but successfully cope with its symptomatic manifestations. Based on the severity, immunotherapy, surgical or cytostatic procedures are prescribed, or combined protocols are used.
Fungal diseases
Another common pathogen, passive carriers of which are about 50% of people, is the Candida fungus. Its activity is associated with a deterioration in the functions of the immune system. Treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa depends on the type of candidiasis – in accordance with the current classification, there are several varieties.
Thrush
Excessive dryness of the inner surface of the tongue, cheeks, and lips, as well as the formation of a white coating. Accompanied by discomfort and burning, often observed in patients of a younger age group.
Atrophic form
The most painful pathology is associated with extensive redness of the affected areas. It covers the palate and corners of the mouth, creating difficulties in the implementation of speech function, as well as inconvenience when eating.
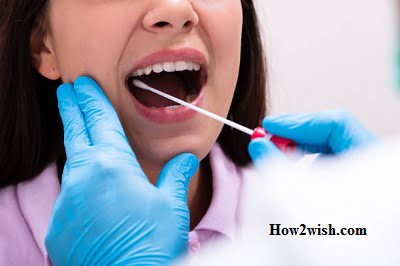
Hyperplastic candidiasis
It is characterized by the appearance of a thickened superficial bacterial layer, during the removal of which there is a high probability of bleeding in the affected areas.
Lichen planus
An ulcerative anomaly, the signs of which, in addition to changing the natural shade, are the emerging vesicles and plaques. It often acts as a side effect of liver disease, diabetes, and disorders in the gastrointestinal tract.
Other types of diseases
There are other diseases of the oral mucosa that do not belong to this classification. One of them is dysbiosis, which occurs against the background of the systematic use of antibiotics or the use of antiseptics. Typical symptoms are the appearance of a persistent unpleasant odor and cracks in the corners of the mouth, however, with prolonged development, there is a possibility of a violation of the structure of the enamel coating of the elements of the dentition. Treatment is aimed at normalizing the internal microflora and is prescribed on an individual basis.
Diagnostic measures
Modern techniques used in dentistry allow you to quickly identify infectious or fungal diseases of the oral mucosa. It is worth noting that self-diagnosis, as well as subsequent attempts at self-treatment, often cause a deterioration in the general condition. Determining the causes of pathological changes is a medical task, for which the following are used:
- Microscopic examination of samples.
- Allergen testing.
- Tests for the presence of viral pathogens.
- General examination and study of anamnesis.
Timely diagnosis is necessary for the preparation and implementation of a correct treatment plan that eliminates both negative symptoms and the factors that turned out to be the cause of pathological changes.
Treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa
The list of procedures prescribed as part of a therapeutic course depends on the specifics of the pathology. The standard protocol includes:
- Professional teeth cleaning, during which deposits are removed from the surface of the enamel, which is the source of the spread of pathogenic bacteria.
- Medical recovery is aimed at stopping painful manifestations and normalizing the general condition.
In difficult situations, surgery may also be required.
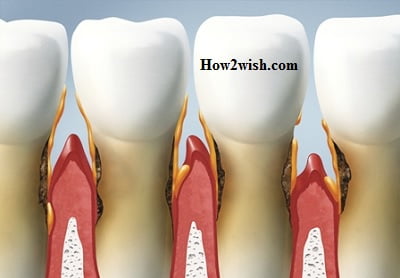
Removal of plaque and calculus
Inflammation of the gums is most often caused by insufficient hygiene care, which results in the accumulation of harmful elements. Hardening deposits form pockets – open areas between the soft tissues and the tooth’s surface, through which the infection penetrates into the periodontium. The use of professional equipment allows you to restore the natural status of the jaw region, preventing diseases of the mucous membranes on the cheeks, gums, and tongue.
General and local therapy
Normalization of the functional state of the immune system involves taking a vitamin complex in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs. In the early stages, it is allowed to independently perform the prescribed procedures at home.
Splinting of teeth
Increased mobility of the elements of the dentition indicates a weakened periodontal structure. To prevent shifting and falling out of units subjected to daily stress, the imposition of splints made from fiberglass tape and a filling compound allows.
Surgical operations
The formation of deep – up to 10 mm – periodontal pockets requires radical intervention. To prevent further spread, curettage is prescribed – instrumental removal of granulations and plaque, implemented in an open or closed way. To determine the degree of development of the disease of the oral mucosa, a photo taken using x-ray equipment helps.
Prevention measures
To reduce the likelihood of the formation of most known pathologies, it is enough to follow simple medical recommendations:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day, preferably after meals.
- Use dental floss and mouthwash.
- Make a balanced diet and give up bad habits.
For a timely diagnosis, you should also undergo a scheduled examination every six months, without neglecting professional hygienic cleaning.
Summing up
Few patients know what this or that disease of mucous tissues is called, and what symptoms can be considered a pathological condition. Considering that many diseases in the early stages do not manifest themselves in any way, regular diagnostics become the only option that guarantees not only the detection of anomalies but also the prevention of the consequences of their development. Specialists of the dental center “Dentika” will take care of the health of your teeth and help you maintain an attractive smile for many years.