What Is An Overbite How Can It Be Correct? Consider one of the most common dental anomalies. Distal occlusion of teeth is a problem that occupies approximately 20% of cases of total jaw pathologies in adults and 30% in children. Therefore, you need to figure out what this violation is, why it occurs, what threat it poses, and, most importantly, how to eliminate it and minimize the consequences.

Immediately, we note that the characteristic symptoms appear at the age of 4-16 years. If they are ignored and no measures are taken, various complications can begin, up to facial asymmetry, difficulty chewing and swallowing, and inflammatory diseases. It is worth preventing the development of this anomaly, and even better – completely getting rid of it.
What is a distal bite (occlusion)
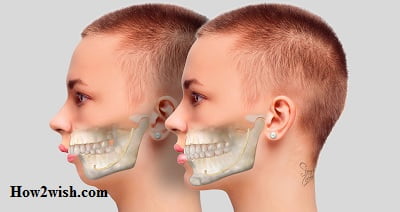
This is a pathology in which the upper jaw is not located on the same level as the lower one, but is significantly advanced, as a result of which the teeth do not close correctly, with an offset. And not only the front ones but also the lateral ones, which creates a block that prevents the healthy development of all incisors.
It arises and develops due to one, several, or a whole group of interrelated factors (will be discussed in detail below), which entails other anomalies, most often a diastema. Also, over time, it causes a weakening of the masticatory muscles, a violation of the respiratory system, and other complications that are dangerous for the body.
Signs of distal bite
It is quite possible to identify occlusion on your own, and not only by the wrong position of the teeth when closing, but also by other signs: by certain facial features, facial expressions, and even by body position or behavior. There are so many nuances that they can be divided into 3 main types.
Intraoral
It is relatively easy to determine the anomaly by the upper frontal incisors. Normally, they should overlap the lower ones by about one-third. In case of violations, they are lowered more strongly, and even pushed forward – so much so that there is some distance between the rows, in the scientific language, it is called the sagittal fissure.
External
Thinking about how to correct a distal bite in an adult (or at least sign up for a consultation with an orthodontist) is worth it if:
- The profile of the face is convex, “bird”;
- The chin is disproportionately small, oblique, with an impressive fold;
- The nose, small in itself, protrudes considerably;
- In a relaxed state, the lips do not close.
The problem is also reflected in the posture: the body is always slightly tilted, the neck seems longer, the stomach sticks out, and the shoulders are hunched.
Functional
If a person has this disorder, it is more difficult for him to breathe through his nose, chew food, swallow, and even speak (often fuzzy diction, lisps). Although usually, he does not notice these inconveniences, since the anomaly develops gradually, from the age of 4-6 years, and the body simply adapts to it.
How to identify distal bite: symptoms of occlusion
The most characteristic signs, especially for non-specialists, are facial, caused by the improper skeletal formation and unbalanced development of the neck muscles. Because of this, the so-called bird profile arises with distorted proportions and a retraction of the lower lip.
There are also more specific, but still quite noticeable points:
- Protrusion (protrusion) of the frontal incisors;
- Insufficient closing of the teeth of the lateral group.
Since the anomaly progresses from a very early age, the child gradually develops infantile swallowing and mouth breathing. The chewing muscles are not strengthened well enough, the functions of the TMJ are weakened over time, and all this provokes the appearance of periodontal and dental diseases.
What causes distal bite: causes
There are several factors that are to blame for this, some of which play their role even before birth, with the growth of the fetus, others have an impact during the first years of life, and others – when growing up. Some of them are controllable, some can be prevented. But in the general case, the formation of pathology is the result of a complex effect of several factors at once.
genetic
Statistics say that in about 2/3 of cases, the anomaly is inherited. And, if there is a predisposition, the “bird” profile and other characteristic features will manifest themselves at a very early age. If it is present, it is especially important to carry out prevention and take measures without delay, otherwise, the violation will only worsen.
Features of intrauterine development
With the growth of the fetus, the jaw may not form correctly – due to the poor health of the mother, which worsened due to the following problems:
- Family or acquired diseases;
- Drinking alcohol, smoking;
- Chronic lack of vitamins;
- Increased background radiation in the place of residence.
As well as adverse environmental factors.
Errors at the stage of feeding and early development
Parents may have to think about how to treat an overbite in a child if they immediately begin to give him not a breast, but a bottle with a wide neck. Because normally the bottom row of a newborn’s incisors is somewhat pushed back compared to the top row, it levels off during the first months of life, when the baby makes intense TMJ movements while feeding. But with unsuitable dishes, there is simply no sufficient load, so the joint is not strengthened, resulting in an anomaly.
In addition, it is better to wean children off the pacifier before they are 2 years old. If they use the nipple for too long, this can lead to the appearance and/or enlargement of the sagittal fissure. And finally, foods with moderate hardness should gradually appear in the diet of a growing baby – so that he trains to chew, and with it the TMJ.
Children’s diseases
Distal open bite of the lower jaw can develop under the influence of the following ailments that appeared at an early age:
- Pathologies of the respiratory tract – from a deviated septum to rhinitis and adenoiditis, leading to the fact that the child draws in and releases air, not through the nose. As a result, his mouth is always open, the joint “gets used” to this position, and an anomaly occurs.
- Problems that disrupt the normal development of the body – a lack of calcium or fluorine, rickets – in a word, everything that can negatively affect the growth and strengthening of the TMJ.
Caries, premature loss of milk teeth
If the anterior and/or lateral incisors fall out too early or, moreover, were torn out by inexperienced dentists, this can also negatively affect the jaw.
Classification of distal occlusion: description
Experts divide this pathology into several subclasses – according to systems developed by reputable orthodontists. Let’s consider them.
Forms according to Khoroshilkina
- Skeletal (gnathic) – the pathology is explained by the disproportionate size or asymmetrical position of the jaws (relative to each other or the skull).
- Dentoalveolar – the anomaly is due to the incorrect growth of individual incisors or the incorrect development of the oral cavity (specifically, the alveolar process, hence the name).
- Mixed – the violation is caused by two of the above problems at once.
Angle subclasses
- I – the top row is pushed forward and, less often, slightly up – a characteristic feature of this case is the presence of a sagittal fissure.
- II – the opposite situation, that is, the incisors look back, and there is no gap between them.
- Whatever the etiology and forms of distal occlusion of the teeth, such a bite is always a pathology in which there is nothing good, and the photos that can be found in any source confirm this.
Consequences
Incorrect closure results in an uneven load on the TMJ. As a result, a variety of dental problems arise – one, several, or all at once from the following list:
- Inflammation and recession of periodontal tissues, and gum pockets;
- Chips and premature abrasion of enamel;
- Pulpitis and periodontitis;
- Weakening and mobility of the roots.
Against this background, gastrointestinal disorders develop, because food is processed relatively poorly. And all because some incisors are overly involved in chewing, others are slightly less involved, and still, others do not participate in this process at all.

Diagnostics
Before proceeding to surgical intervention or choosing a bracket system, you need to make sure that this is a distal occlusion: treatment in adults and children, especially surgical treatment, can only be prescribed based on the results of a comprehensive examination.
First of all, doctors need to conduct a complete clinical examination:
- Listen to complaints and collect anamnesis, including lifestyle information, and analyze it.
- Examine the oral cavity, gums, hard palate, and mucous membranes of the patient, palpate the TMJ, and identify violations.
- Conduct a functional test of Eschler-Bittner and evaluate the profile of the face.
After that, for clarification (if it is required), orthodontists send a person for an x-ray. In addition to profile and full-face images, specialists will take impressions and generate control models to determine the state of the TMJ and the degree of impairment as accurately as possible.
What is Dental Pulpitis, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
To prescribe the correct treatment for distal deep occlusion of the dentition, the patient may also be required to do an orthopantomogram and a teleroentgenogram in a lateral projection. With the help of the first, the state of the chewing apparatus and hard tissues, the changes that have already taken place, and the relative position of the incisors, deviations, and asymmetry will be determined. Thanks to the second, the type of anomaly will be established according to the classification of Khoroshilkina.
Having examined the TMJ, specialists will find out how the articular heads are placed about each other, whether the gap between them is normal, or whether its expansion already threatens disorders and dysfunction.
The more voluminous the diagnosis, the more accurate the anamnesis, and hence the decision of the doctor.
Treatment of distal occlusion in children and adults without surgery
It is prescribed only after the type of pathology is established and concomitant diseases are identified. The diagnosis indicates the main anomaly, problems of bone and soft tissues, and individual incisors. In the appendix – additional violations, for example, difficulty in breathing.
After that, specialists choose the method of influence: it can be therapy with the use of modern fixators, the use of devices, and the performance of multifunctional exercises, or, less commonly, surgical intervention. Therefore, first of all, we will consider options that do not involve radical measures.
A child with mixed dentition
In such a situation, various devices are the most effective – doctors prescribe wearing designs of locks and arches that help the incisors to take the correct position:
- Frenkel regulators;
- My gymnastic clamps, push the lower row to the same level as the upper one;
- Screw activators.
Yes, there are also difficult cases, for example, microdontia. Then it remains only to remove the incisors according to Hotz: dairy – at the age of 7-8.5 years, small indigenous – at 10-11. Due to this, there will be enough free space for the normal growth of permanent canines. It is also necessary to remove premolars in case of macrognathia, and this is exactly the option when surgical treatment of deep distal bite continues with distalization and the use of braces.
In a child with temporary incisors
The development of pathology can be avoided if the baby is properly fed from birth (the absence of bad habits in the mother is implied), and also follow all the recommendations of doctors. After the first months of life, you need to gradually teach him to chew, carefully watching how his TMJ works. Such a responsible approach will also help to avoid problems with swallowing, breathing, and articulation.
If the violations still manifest themselves, you need to make an appointment with an orthodontist for a consultation. It is recommended to do this from the age of 3 years. The specialist will diagnose and, in the absence of serious violations, select a removable simulator, prescribe my gymnastics, and the like.
In adults
Is it possible to correct the overbite with braces after 20, when the jaw has already formed? Yes, but only with the dentoalveolar nature of the anomaly. In other cases, the impact is different:
- If the upper row is seriously narrowed, the least valuable incisors are removed with the Derichsweiler apparatus;
- When the pathology is gnathic, the osteotomy is performed, and the result of this surgical intervention is fixed with special fixators;
- In case of skeletal disturbance, the structure of arches and locks is supplemented with rubber traction.
Any of these solutions continues with a long retention period (2-3 times longer than the therapy itself). It is mandatory, because otherwise the incisors will want to return to their original, albeit incorrect, places, and there is no need to talk about any quality of the result.
Terms of treatment
It all depends on the method of exposure, age, and nature of the anomaly. For example, correction of distal occlusion in adults with braces takes 1.5-2 years, not counting the recovery of 3-5 years. Yes, it’s long, but it’s a serious problem. In adolescents, everything is a little easier, due to a decrease in the retention time, but they will also have to vilify orthodontic structures for 18-24 months.
Preventive actions
In the presence of unfavorable genetics, they are carried out from the cradle. But even if everything is in order with heredity, you need to do the following:
- Ensure proper feeding;
- Timely transfer of the baby to food of moderate hardness;
- Gradually wean from the nipple;
- Prevent too-early removal of milk incisors;
- Immediately and effectively fight somatic diseases and inflammations;
- Exclude factors that provoke violations of posture, swallowing, and breathing.
When evidence appeared that the problem did arise, it is necessary to contact the orthodontist. If he confirms his suspicions, he will pick up an apparatus, for example, a Dass or Rogers activator, a spinner, or a vestibular shield. If an anomaly is observed with temporary incisors, it may be a trainer or a similar design – a Katz bite plate, a Stockfish kinetin, or a Khoroshilkina-Tokarevich violator.
Summing up
We examined in detail how dangerous distal bite is, what adults should do, how to fix it in a child with braces, and the like. Two conclusions can be singled out at once: firstly, this is a pathology that needs to be fought, and there are effective means. Secondly, this is a violation that is quite realistic to prevent, so it is very important not to neglect prevention.