Diastema is one of the most common pathologies. According to official statistics, every fifth inhabitant of the planet has a gap between the front teeth. In a sense, this is considered one of the variants of the norm, it is not a deviation to be eliminated. Especially if the distance is small. However, in the opposite case, this phenomenon does not require mandatory dental intervention. Although it often causes enormous inconvenience to its owner, it provokes serious psychological discomfort. In such a situation, the only way out is to seek help from an orthodontist.
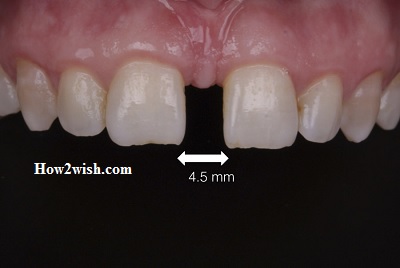
Diastema between teeth – what is it, and how to get rid of it
The disease is expressed in the form of a large gap between the anterior central incisors, which can affect both the upper and lower rows. The average width of the resulting gap is about two to six millimeters, it all depends on individual characteristics.
In fact, this is the same dentoalveolar pathology as all the others: excessive sizes of crowns, dental curvature, abnormal location, etc. In the vast majority of cases, it is hereditary and occurs due to a genetic predisposition. Less commonly, the factors determining development are some kind of mechanical damage and bite problems.
The need for professional dental intervention depends on the severity of the disease, as well as the process that provoked its appearance. The same grounds influence the choice of treatment and rehabilitation programs. The most popular correction method is the installation of braces or overlapping with veneers. Surgical manipulations are practiced extremely rarely.
Etiology
In the vast majority of cases, the causes of diastema are uncontrollable and uncontrollable factors – heredity, and congenital dentoalveolar anomalies. However, along with them, there are other prerequisites:
- Unfavorable gene set;
- Pathological curvature of the lateral incisors;
- Abnormal size of the front teeth;
- Premature or, conversely, belated change of dairy rows;
- Violations of the structure of the frenulum;
- Pronounced incommensurability of the jaw and dental elements;
- Chronic diseases of periodontal tissues.
It is important to understand that imperfection is not always innate, it can manifest itself over time. This process is driven by a range of factors. So, for example, in children, gaps are formed due to the abuse of bad habits. What exactly? Suck your thumb or chew on the ends of stationery.
To draw up a corrective program to eliminate the gap between the incisors, it is necessary to understand the underlying fundamental causes of its occurrence. In addition, it should be understood that in some situations this defect cannot even be called a pathology, it seems to be one of the variants of the norm. For example, a diastema appears if a person develops small teeth with fairly wide upper gums. Professional dental intervention in this case is not required. The problem is purely aesthetic.
We discussed the bad habits of children, but what about adults? They have a gap formed as a result of the loss of molars. The fact is that the human body always strives for some kind of ideal state. That is why when some elements disappear, others gradually fill in the resulting voids.
Occlusion pathologies and congenital dental curvature are other common causes of disease progression. They need regular preventive examinations at the dentist and maintenance therapy.
Classification
It is important to understand that a defect can be considered in several classification sections at once. So, for example, the phenomenon is analyzed from the point of view of a specific stage of development:
- False – when the milk bite changes;
- True – when permanent molars appear.
In the first case, the problem does not need professional intervention, it disappears on its own as the dentition is renewed. Second, elimination is possible only through qualified dental care.

The next principle of division is based on location. There are two forms:
- Symmetrical, in which the incisors are at an equal distance;
- Asymmetric, when there is an uneven displacement of the crowns.
Also, classification can be made based on the features of the lateral slope, medial curvature, and the like.
False
It is diagnosed in children during milk eruption. It is eliminated as the dentition is filled.
True
It is observed when teeth are renewed for permanent molars. Diastema call all cases when the distance exceeds the mark of one millimeter.
Physiological
Appears during the period of active growth and formation of the jaw. Sometimes it is indicated faster than the incisors have time to grow. It is important to ensure that the gums are not injured, as soft tissues are in a vulnerable position.
Pathological
It is provoked by the atrophy of the spongy jaw bones or a lack of units in the dentition. One of the reasons is the early removal of the milk elements, caused by the improper development of the root primordia. Requires qualified dental treatment.
Commonly associated symptoms
It is quite difficult not to notice the imperfection – the gap is located in a prominent place, and it immediately catches the eye. As noted earlier, the distance between the anterior incisors is uniform or widening towards the lower edges. In the latter case, a certain triangle is formed, which is not recommended to be ignored, even if you perceive the gap as your own highlight.
The thing is that such an arrangement is considered abnormal, increases the curvature of occlusion, and leads to the development of bite pathologies – mesial, distal, open, or cross.
If we talk about concomitant symptoms, then this includes:
- Distortion of the reproduction of hissing sounds;
- Lisp;
- Discomfort, increased sensitivity of the gums;
- Violation of the structure of periodontal tissues.
In general, ignoring the pathological phenomenon is associated with a huge variety of complications and negative consequences.
How to diagnose
To make a diagnosis, it is enough for the dentist to conduct a comprehensive visual examination. Additional analyzes or research activities are not required. If the patient intends to eliminate the problem and wants to get a beautiful smile, a more thorough study of the clinical picture is necessary.
First of all, the features of the passage of the central line are revealed, the types of the defect are determined, as well as the causes of its occurrence. Standard diagnostic procedures include:
- X-ray examination;
- Removal of jaw casts;
- Analysis of the location of the incisors;
- Estimation of slot symmetry.
Sometimes additional corrective methods may be involved in dental practice. However, they are more typical for orthodontists than for surgeons and orthopedists.
Methods for the treatment and correction of dental diastema in adults
Above, we discussed in detail the possible clinical manifestations and options for diagnosing pathology. So, in the overwhelming majority of cases, it is possible to confine ourselves to a banal visual inspection, without resorting to third-party manipulations. If a person intends to eliminate the defect and wants to get an even and healthy smile, additional examinations are required. Their general mission is to analyze the condition of the incisors.
visit this related post Everything You Need to Know About Treating a Cyst in Your Tooth
Based on the information received, one of three treatment directions is selected. Next, we tell you how to remove diastema in adults and children.
Aesthetic restoration
Disassembled diagnosis provides a huge variety of options for correction. When it comes to aesthetics, there are two key techniques:
- The use of veneers. In this case, the front incisors are covered with thin plates made of ceramics. As a rule, their thickness does not exceed 0.7 millimeters. They help to make the restoration as comfortable and invisible as possible. Such designs quickly correct the shape of the units, making the smile even and beautiful. However, they have a significant drawback – the need for turning the enamel.
- Crown prosthetics. All the same, fangs-cutters are subjected to strong grinding, and then they are closed with caps-crowns – all-ceramic or metal-ceramic. They exactly repeat the anatomical structure of the teeth, ensuring their return to the correct location. Of the materials, zirconia is the best.
In fairness, it should be noted that the analyzed methods are used exclusively in adulthood. Less severe options are practiced with children. We will talk about them further.
Surgical intervention
As a rule, surgeons resort to help only in those cases when the pathology developed due to the abnormal shape and size of the frenulum. Then a complex plastic is necessarily carried out, an individual orthodontic recovery program is drawn up.
Another reason for organizing such serious dental events is corticotomy. This term is used to refer to the simplest operations carried out in order to change the location of the teeth as part of the treatment cycle. The point is to make several incisions in problematic jaw areas. This helps to soften the bone tissue and to carry out all the manipulations that require the least trauma.
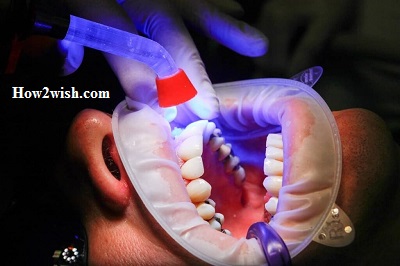
Orthodontic therapy
The most common and effective method of correcting the situation is correction with braces. Representing non-removable orthodontic structures, they can be installed from adolescence. In early childhood, they are not used, since the process of changing the milk bite has not yet been completed.
When it comes to pediatric orthodontics, generally uses more gentle and less painful corrective techniques. For example, removable plates or structures designed to fix the central incisors. When the problem is hereditary, it is obvious from birth, it is recommended not to hesitate with therapy. Over time, it will only become more difficult to eliminate imperfection.
One of the patient reviews:
“I remember that I suffered for a long time with a gap, and then, finally, I found“ my ”doctor! He put braces on me, and within a year everything was fixed. Now the teeth are even, the smile is beautiful. And what was – scary to remember! A huge gap in the upper jaw, and even trema all over the bottom row. Before that, I didn’t smile at all, but I tried to talk with closed lips. Fortunately, all this is over!”.
Remarkably, innovative bracket systems are made from high-strength materials that perform well in operation. It can be classic metals or more aesthetic ceramic and sapphire settings – the choice is incredibly wide. As for fastening the staples, they are placed throughout the jaw or within a specific area. Sometimes a variant of the lingual system is practiced – it is attached to the back of the dentition. The solution is expensive but causes the least discomfort.
How to remove the diastema of the anterior lower teeth: photo problems in childhood
When carrying out diagnostic measures in a child, the specialist, first of all, finds out the nature of the disease – whether it is false or true. For this, a comprehensive x-ray examination is organized, after which the images are studied by the commission. Based on the materials studied, a verdict is issued. If the seam between the incisors is clearly visible, a decision is made on corticotomy – it allows you to fill in the missing gaps of bone and connective tissues. Surgical intervention is reduced to the correction of the palatine region, bringing it to a normal state. Remarkably, any manipulations are carried out exclusively under anesthesia. It is recommended to be prepared for the fact that the rehabilitation period will take a long period of time, it will be accompanied by rather uncomfortable sensations.
However, modern pediatric dentistry also offers less painful treatment options – for example, the installation of a retainer made of carbon threads. As part of this method, the attending physician carefully threads a special rubber structure through the incisors, fixing it for about seven to eight days. Then it is removed and replaced with special fixing elements, with which the child walks for about a year.
When the pathology is provoked by the excessively large size of the milk incisors, their early removal can be prescribed. Although the measure is recognized as radical, it has a quite tangible effect. And quickly and effortlessly.
Trema and diastema – what’s the difference
Despite a common misconception, these terms are not synonymous. Pathology-trema is diagnosed in cases where the tooth gaps are excessively wide. As a rule, we are talking about the distance in the entire length of the top or bottom row. Systemic manifestations apply exclusively to the anterior incisors.
Thus, the main difference is the location of the defect.
Prevention – how to prevent the appearance of a gap
When diastema is a hereditary phenomenon, it will not be possible to prevent its formation. If unwanted distance was not present at birth, you can prevent its occurrence in the future. This requires regular visits to the orthodontist, fulfilling all appointments, follow the advice and recommendations.
So, what preventive measures will help achieve the goal?
- Give up bad habits. If we are talking about a child, help him stop sucking his thumb, biting his nails, and putting pens and pencils in his mouth.
- Carefully monitor oral hygiene, and keep it in optimal condition. Choose quality cleaning products that will not allow pathological changes in the gum and periodontal tissues.
- Visit your local dentist every six months. This is especially true if there is a genetic predisposition.
Now you know everything about what to do with diastema, and how to fix it. We hope that the presented material was useful, and helped to find answers to your questions.