What is a dystopia tooth, is it a problem that requires radical medical intervention, or an aesthetic defect that can be ignored? The therapeutic tactics were chosen by the dentist depending on the age of the patient, the localization of the pathological element, the availability of free space in the row, and the location of adjacent crowns.
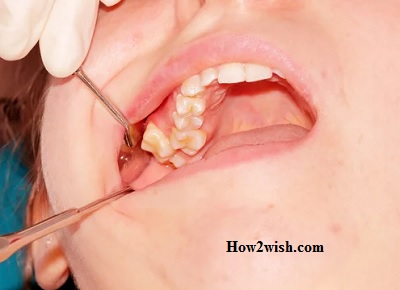
Pathology develops for various reasons, the most common of which is a hereditary factor. However, such violations can be prevented by observing simple preventive rules.
What is dystopia
This is a deviation characterized by an incorrect arrangement of units in the dental arch or outside it, as a result of which the eruption of the next incisors, canines, and molars is complicated. In dentistry, each element corresponds to a certain position in the row. If the process occurs with deviations from the norm (crowns deviate, roots grow together, etc.), this brings aesthetic discomfort, pain, and other unpleasant sensations. The problem does not always need to be solved by radical methods, however, there is a list of indications when surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
The concept of retention
What does dystopia impacted tooth mean? In addition to the deformation of the unit, there is a violation of the timing of the eruption. For the incisor, canine, or molar to reach the surface of the gums, it is necessary to eliminate the factors that prevent this. As a rule, problems with bone or soft gum tissues lead to this phenomenon. There are 2 types of pathology:
- Partial (the dental unit did not come out completely);
- Complete (the crown did not appear, and the germ remained in the bone structures).
The pathological process occurs in persons of any age category and gender. Most often, it concerns the “eights”, but the retention can also affect other elements. Usually, disorders appear symmetrically, that is, on both sides of the upper or lower jaw.
Thus, the impacted tooth is not only crooked, but it also cannot erupt normally. Such deformations cause inflammation and pain in the patient. Most often, surgery is required to prevent such problems with neighboring dental units. After extraction, the molars, canines, and molars grow without disturbance.
Often this type of disease is accompanied by a malocclusion.
Dystopia classification
Pathology is divided into congenital (is hereditary or develops in utero) and acquired. In the latter case, the problem occurs after birth.
In addition, improperly developing dental units are divided into 2 types:
- With bone immersion (located in the jaw bones);
- With tissue (found in soft tissues).
If the problem is partial, the location of the crown does not change much. Complete displacement is accompanied by the exit of the coronal part beyond the socket and retention solely due to the gums. In a separate type, trauma is distinguished, which occurs as a result of mechanical action.
Classification by the nature of the displacement:
- In the sagittal and transversal planes;
- Vertical arrangement;
- Torso position and transposition.
Why does pathology develop
When conducting numerous medical studies, it was found that there is a list of provoking factors that lead to dystopia. The process of laying, growth and development of dental units in the fetus is affected by the gynecological diseases of a woman during childbearing. For example, this includes toxicosis in the 1st trimester of pregnancy and iron deficiency anemia. In addition, infectious processes (not only in the genitals), but bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse) in the expectant mother are also extremely dangerous.

Dystopia incisors, canines, and molars may be irregular in shape and anomalous in size. The likelihood of retention, over-completion, and dementia increases.
All reasons are divided into 3 large groups:
- Intrauterine. These are infections, metabolic disorders, rickets, lack of vitamins, problems with the thyroid gland, etc.
- Phylogenetic. This includes changes associated with evolutionary transformations of the dentoalveolar system. Since the jaws become smaller over time and the row structure does not change, there is little room for new units and their proper development.
- local factors.
The latter category includes many external and internal causes, such as:
- Infection of the rudiments of permanent occlusion with periodontitis of bone elements in the dairy;
- Delayed eruption in the first year of life;
- Fusion of the root parts located in the neighborhood;
- Loss in preschoolers ahead of time;
- Mechanical impact;
- Cementomas (slow-growing, cement-like tumors);
- Too deep laying of the follicle in the jaw;
- The formation of follicular cystic neoplasms;
- Tumors that force out uncut rudiments.
Signs of retention and dystopia
Symptoms cause a person severe discomfort. The severity of sensations depends on the localization of the problem and the degree of deformation of the unit. Typical symptoms:
- Injury to the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- Accumulation of a dense layer of plaque due to insufficient hygiene;
- Problems with speech, chewing food;
- Formation of malocclusion.
If the impacted crown is completely closed, this will not lead to the appearance of pronounced signs. However, in areas of contact with soft tissues, cervical caries, periodontitis, pulpitis, inflammation, suppuration, and cystic formations can occur. A medical examination reveals protrusions of the gums, as well as voids in the alveolar arch.
The Guide to Strengthening Tooth Enamel and Maintaining Good Oral Health
When dystopia teeth are strongly tilted, this leads to injury to the inside of the cheeks, tongue, and lips. Open wounds are often infected with pathogenic microorganisms, so inflammation very often accompanies dystopia. In severe cases, there are serious violations of diction, the patient cannot fully chew food.
Diagnosis of the disease
Since the problem is predominantly aesthetic, you can detect violations on your own without special knowledge, simply by examining the oral cavity. In any case, if a person notices signs of wisdom tooth dystopia (in dentistry, this can be a canine, premolar, etc.), it is necessary to contact the clinic. Specialists use various techniques, including hardware research.
What is required for an accurate diagnosis:
- Visual examination in the dental chair;
- Orthopantomography (panoramic image of all jaws and nearby elements of the facial skeleton);
- Teleroentgenogram (obtaining an image of the whole skull on a scale of 1: 1);
- Making casts to create models (this way you can assess the condition of the maxillofacial apparatus and perform the required measurements);
- Bite examination, identification of possible problems, and development of further therapeutic tactics;
- Collection of the patient’s history.
Difficulties arise in cases where eruption has not yet occurred, but there are suspicions of abnormal growth. In such situations, computed tomography is indicated.
Principles of treatment: is it possible to avoid surgery
To develop the right therapeutic tactics, several points must be taken into account at the same time:
- Patient’s age;
- Location and type of dystopic unit;
- The presence of free space in the dentition;
- Position of other incisors, canines, and molars.
After a thorough diagnosis, the doctor chooses one of two intervention options: repositioning or extraction. In the first case, we are talking about the return of the tooth to its place. This type of intervention is most suitable for the treatment of adolescent patients. If there is free space in the arch, everything is aligned with the help of braces, mouthguards, plates, aligners, etc. Orthodontic structures can be both removable and non-removable.
This is the longest method of treatment because even after dismantling the system, the orthodontist will install retainers to consolidate the result. The fact is that the problem can recur.
The main principles that guide the dentist when deciding on therapeutic methods:
- Pathological “eights” are usually removed. This is especially recommended when injuring adjacent units. However, the procedure can lead to a dislocation of the jaw and bleeding.
- All manipulations should be carried out in stationary conditions, followed by a rehabilitation period.
- In the absence of free space, braces are installed.
- Fangs take an active part in the process of chewing, so doctors strive to save them. Usually, the adjacent premolar is pulled out, and a retainer is applied to prevent a recurrence.
- When injured, tires and ligatures are used. If the extraction cannot be avoided, prosthetics are subsequently performed, and implants are implanted.
- If there is no aesthetic problem, it is better to leave everything as it is. When soft tissues are injured, grinding of sharp tips will help.
Dentists try to preserve pathological units as much as possible. If tearing out cannot be avoided, it is important to establish artificial analogs as soon as possible.
Extraction of an abnormal tooth
In what cases in the dental clinic resort to extraction:
- Swelling and soreness of soft tissues;
- Periostitis, pericoronitis, osteomyelitis during the formation of a hood over the “eight”;
- Carious formations in the neighborhood;
- Numbness in the face due to excessive pressure of incisors, canines, and molars that have not
- Erupted to the end on the nerves;
- The need to free the vacant area for subsequent prosthetics and perform various manipulations by the orthodontist;
- High risk of displacement of nearby dental units;
- Periodontitis, pulpitis in a chronic form.
When removal is contraindicated:
- Exacerbation of diseases associated with the functioning of the nervous system;
- Serious condition of the patient;
- Infectious process in the advanced stage;
- The period after ovulation immediately before the start of the next menstrual bleeding;
- Blood diseases;
- Acute or exacerbated chronic cardiovascular pathologies.
Surgical intervention involves the passage of successive stages:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity. Eliminates caries and other pathological processes.
- Anesthesia (anesthesia).
- Violation of the integrity of soft tissues to get to the cavity.
- Preparation for the operation.
- Direct extraction.
- The imposition of suture material.
In the treatment of dystopia of the upper, and lower canines, they usually try not to pull them out. They are of greater value than the rest of the units. If there is no free space in the row, the first premolar is removed.
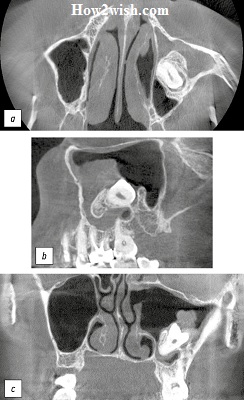
If a dislocation occurs, the doctor anesthetizes the victim, then carefully sets the arc elements in the right place. Fixation is carried out with the help of ligatures made of wire or tires. Complete trauma requires removal with subsequent implantation of implants and the installation of prostheses.
During pregnancy, it is advisable to postpone the procedure until delivery, preferably until the end of breastfeeding. If this cannot be avoided with the abnormal position of the wisdom tooth, then it is better to visit the surgeon in the 2nd or early 3rd trimester of gestation.
Features of care after surgery
Rehabilitation is not as easy as it seems at first glance. If the dentist has not developed an individual therapeutic regimen, the following recommendations must be observed:
- Give up within 3-4 hours after surgery from drinking, eating, do not rinse the mouth, not smoking;
- In the recovery period, take good care of the mucous membranes, perform regular hygiene procedures;
- Refrain from using special rinses for several days;
- Do not play sports for up to a week;
- Avoid exposure to too high and low temperatures, including during meals;
- Gently chew food with the healthy side of the jaw;
- Exclude alcoholic beverages.
Doctors often prescribe antibiotics and painkillers. Patients are advised to rinse their mouths with chlorhexidine. To prevent negative consequences, it is important to follow all medical prescriptions.
How to avoid complications
Severe swelling may occur for 2-3 days. This is normal and will gradually go away. If everything went well, after a week there will be no trace of edema.
Often the wound bleeds for a while. To stop it, special medicines are placed in the hole. To avoid adverse reactions, doctors advise giving up hard, hard food, as well as cold or hot food for a while. Daily hygiene should be gentle but effective.
In what cases should you immediately contact the dental clinic:
- Persistent bleeding;
- Severe swelling of the soft tissues, which does not decrease, numbness of the face;
- Discomfort when opening the mouth;
- The appearance of an inflammatory process;
- Violation of the integrity of adjacent healthy units and gums.
Disease Prevention for Dystopia Tooth
Preventive measures should be resorted to even in the gestational period, that is before the baby is born. Effective measures:
- Passing all necessary examinations, compliance with medical recommendations during pregnancy;
- Breastfeeding for at least six months (preferably longer);
- Timely introduction of products of the first and subsequent complementary foods;
- Prevention of injury to the maxillofacial apparatus;
- PP (foods containing all essential vitamins and minerals);
- Pulling out staggering milk teeth, if the roots began to erupt;
- Refusal to use nipples and bottles for a long time, sucking fingers, biting felt-tip pens and other objects;
- Bite change control;
- Regular visits to a pediatric dentist for preventive oral examinations and professional cleanings.
From the first year of life until the age of 14, it is recommended to visit a dental clinic every six months or even more often. This will help to establish a dystopia planner and take all necessary measures to eliminate it.
In the photo of dystopic teeth (canines, incisors, molars) presented on the Internet, you can see how serious this pathology can be. Incorrect growth of units is not always an exclusively aesthetic problem. A defect can significantly impair a person’s quality of life and interfere with the normal chewing of food, or cause other discomforts. The problem is solved surgically or with the use of orthodontic structures. To prevent pathology, it is recommended to follow simple preventive rules, and then the smile will be dazzling, and the dentition will be even and beautiful.